Message
What is Casting?
Casting is a manufacturing process that involves using molds to create parts. There are various types of casting methods available, and they can be used with different materials. However, this article specifically focuses on metal casting and does not cover other materials like epoxy that may be used in multi-component casting.
In metal casting, the process involves pouring or injecting molten metal into a pre-made mold, which is sometimes called a die. If intricate internal geometries or cavities are required, cores or inserts are used. Once the part cools and solidifies, it undergoes cleaning and processing to achieve the desired surface finish. In certain cases, additional CNC machining may be performed as a secondary operation to further refine the cast metal component and achieve tighter tolerances.
There are numerous metal casting techniques available, which are chosen based on factors such as the selected material, the size and shape of the casting, and other specific properties. Some popular casting methods include die casting, sand casting, pressure casting, and investment casting.
A wide range of parts can be produced through casting, such as turbine blades, train wheels, bus pedals, and engine blocks. Cast parts are utilized in various industries, including aerospace, automotive, consumer products, and medical devices.

Pros and Cons of Casting
Advantages
Casting offers a wide range of design possibilities, allowing for the creation of complex and unique shapes, including intricate internal cavities.
For large production runs, casting can be cost-effective compared to machining. Moreover, casting is faster in terms of production time.
Using reusable molds in casting ensures a high level of repeatability, as identical copies of parts can be created consistently.
Casting is highly efficient in terms of metal usage. Nearly all the metal used in the process becomes a part of the final product. Any excess metal from the pouring process or rejected parts can be easily melted down and recycled.
Disadvantages
Techniques such as die casting and precision investment casting offer high accuracy, but when it comes to precision and achieving tight tolerances, CNC machining is generally the superior choice.
In terms of smaller production runs, the cost per part is typically higher for casting compared to machining.
Producing cast parts often takes more time due to the requirement of designing and procuring molds.
Compared to CNC machining, casting has limitations in terms of the selection of metal materials available.
Cast parts often require additional post-processing steps, such as removing excess cast material or using sandblasting to eliminate burrs.
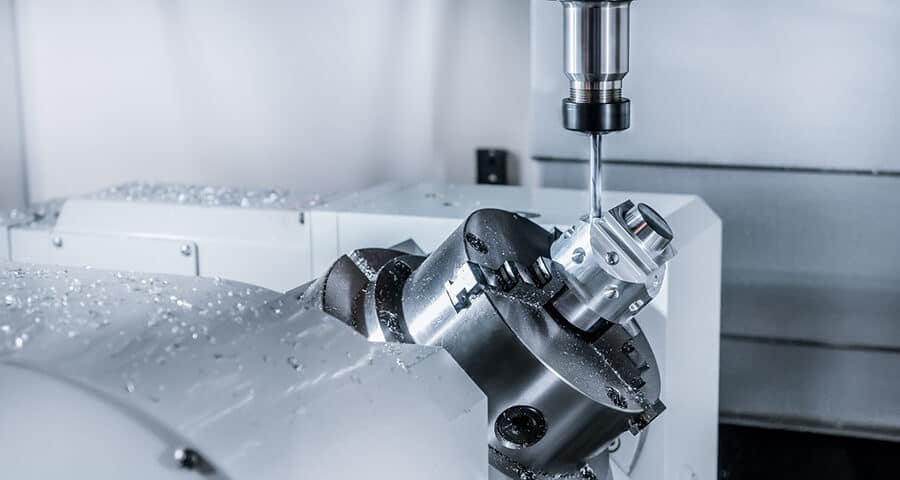
What is CNC Machining?
CNC machining is a manufacturing method that involves using a cutting tool to remove material and achieve the desired shape. To control the machining process, a computer program, often utilizing G-code instructions, is used to guide CNC machines such as mills, lathes, and other equipment. CNC machining covers various types of machining, including milling, turning, drilling, and boring, depending on the specific requirements.
CNC machined parts have widespread applications across different industries. They are crucial in the creation of metal laptop enclosures, small components found in mobile phones, and essential elements used in aerospace and automotive parts. Additionally, CNC machining plays a crucial role in producing fixtures, jigs, and even casting molds.
Pros and Cons of CNC Machining
Advantages
CNC machining is capable of producing highly precise parts that meet strict quality requirements with accurate dimensions and smooth surfaces.
When machining unique or small quantities of parts, it’s generally faster than the casting process.
For small production runs and prototyping, CNC machining usually costs less per part.
CNC machining is compatible with a wide range of metals, making it a versatile process.
Disadvantages
CNC machining is not well-suited for creating internal cavities in parts whereas it’s more suitable for shaping external geometries.
It’s cost-consuming for large batch production but the cost per part remains relatively consistent regardless of batch size in casting.
Certain parts with complex designs or specific materials may require a significantly longer time to machine. As such, CNC machining is not cost-effective for large volumes.
CNC machining can generate more metal waste compared to casting, and the recycling process can be more labor-intensive. Oftentimes, the waste needs to be transported off-site for proper recycling.